Introduction
Introduction to CloudForms
Red Hat CloudForms is an infrastructure management platform that offers a consistent way to track costs, control resource allocation, and ensure compliance across all your networked environments. Manage Virtual Machines, containers, and your clouds in the same way with a single tool.
In this lab we will focus on he Ansible features provided by CloudForms. We will setup the embedded Ansible role, create Service Catalog Items for Ansible Playbooks, and demonstrate how the CloudForms UI can be exteded with custom menus and buttons.
For more details about CloudForms, you can have a look at the General introduction.
Access the lab environment
-
First time login, forgot login or password? Go to https://www.opentlc.com/account
-
Your username should NOT have an @ in it.
-
Partners MUST request access to RHPDS by sending an email to open-program@redhat.com.
-
Passwords to the services is referred as
<to_be_provided>. Please contact GPTE you didn’t get them.
Log into RHDPS and order the Lab from the Service Catalog as follows:
Log in to the Red Hat Product Demo System with your provided credentials.
Go to Services -> Catalogs
Under All Services -> Red Hat Summit 2018, select CloudForms with Ansible Better together!
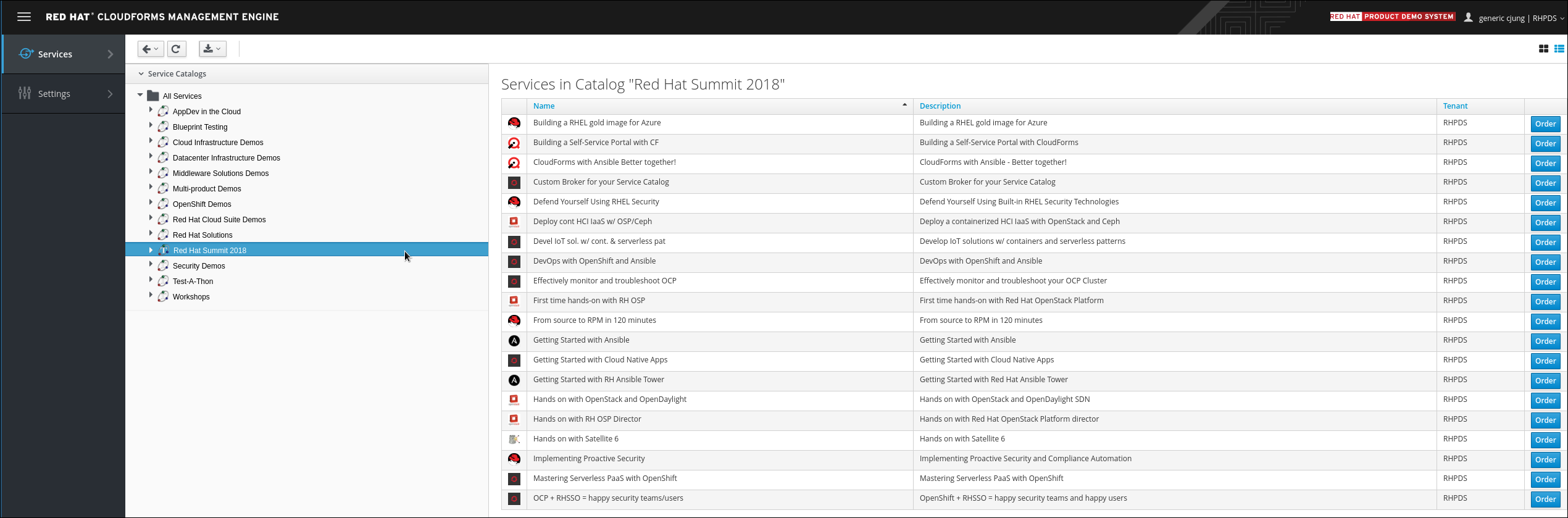
On the right pane, click Order

Please, read carefully all of the information on the resulting page, check the box to confirm you understood the runtime warning message, and then click Submit.
It takes about 20 ~ 25 minutes for the demo to load completely and become accessible. Wait for the full demo to load, even if some of its systems are marked “Up.”. Watch for an email with information about how to access your demo environment. Make note of the email’s contents: a list of hostnames, IP addresses, and your GUID. Whenever you see in the demo instructions, replace it with the GUID provided in the email. You can get real-time updates and status of your demo environment at https://www.opentlc.com/rhpds-status.
Be mindful of the runtime of your demo environment! It may take several hours to complete the demo, so you may need to extend the runtime. This is especially important in later steps when you are building virtual machines. For information on how to extend runtime and lifetime, see https://www.opentlc.com/lifecycle.